CARATTERISTICHE TECNICHE
TECHNICAL FEATURES | CARACTERISTIQUES TECHNIQUES | TECHNISCHE EIGENSCHAFTEN | ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ
CARATTERISTICHE TECNICHE
TECHNICAL FEATURES | CARACTERISTIQUES TECHNIQUES | TECHNISCHE EIGENSCHAFTEN | ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ
SCIVOLOSITA’
La resistenza allo scivolamento è una caratteristica che ricade su sicurezza e salute degli utilizzatori, ovviamente nel caso di pavimentazioni.
Le superfici scivolose sono potenziali cause di infortuni, anche gravi sia in ambito civile che negli ambienti di lavoro. La grandezza che quantifica la resistenza allo scivolamento è il coefficiente di attrito
(statico o dinamico), al quale è proporzionale la forza, parallela alla superficie di contatto, che occorre applicare perchè si abbia moto relativo tra due corpi, e quindi anche la forza che ne definisce
le condizioni di equilibrio. Quanto più alto è il coefficiente di attrito, tanto minore è la scivolosità. Attualmente non è disponibile un metodo di misura standardizzato a livello internazionale, la maggior
parte delle nazioni ha metodi propri derivati da leggi, disposizioni antinfortunistiche o altre regolamentazioni di carattere nazionale. Per aver un buon risultato, il valore medio del coefficiente di attrito
dinamico deve essere: μ>0,40, R≥R9 e μ≥A. Qui di seguito riportiamo la sintesi degli indicatori che misurano la resistenza alla scivolosità:
R: indica l’angolo di inclinazione raggiunto nel test di prova
A.B.C.: sono riferimenti di resistenza alla scivolosità relativa ad ambienti umidi e a piedi nudi.
SLIP RESISTANCE
Slip resistance is a characteristic that affects the health and safety of users in the case of flooring. Slippery surfaces are potential causes of accidents, even serious ones, in civil and work environments.
The value that measures slip resistance is the coefficient of friction (static or dynamic); the force required for the relative movement between two bodies (and therefore also the force defining the equilibrium
condition), the said force being parallel to the contact surface, is proportional to the coefficient of friction. The higher the coefficient of friction, the less slippery is the surface. An international standardised
measurement is not currently available and most countries have their own measurement methods based on laws, accident prevention regulations or other national regulations. For a good result, the average
dynamic coefficient of friction should be: μ>0.40, R≥R9 and μ≥A. Here below a short description of the indicators to measure slip-resistance:
R: angle of slope achieved during testing
A.B.C.: slip resistance indicators for walking in humid areas.
GLISSANCE
La résistance à la glissance du carrelage est une caractéristique très importante pour la sécurité et la santé des utilisateurs et des professionnels pendant la pose du matériel. Les surfaces glissantes sont
potentiellement cause d’accidents, même graves, dans le niveau civil comme professionnel. La grandeur qui quantifie la résistance au glissement est le coefficient de frottement (statique ou dynamique),
qui est proportionnelle à la force, parallèle à la surface de contact, qui devrait être appliquée, car il ya du mouvement relatif entre les deux organes, et donc aussi la force qui définit les conditions
d’équilibre. Plus le coefficient de frottement est grand, moins importante sera la glissance. Actuellement, il n’existe aucune méthode normalisée de mesure de niveau international, la plupart des nations ont
leurs propres méthodes dérivées de lois, règles ou règlements de prévention de caractère national. Pour un bon résultat, la valeur moyenne du coefficient de frottement dynamique, devrait être: μ>0,40,
R≥R9 e μ≥A. Voici un résumé des indicateurs qui mesurent la résistance à la glisse:
R: indique l’angle d’inclination mesurée avec le test.
A.B.C.: sont des valeurs de resistance à la glisse relatives aux niveaux humides et à pieds nus.
RUTSCHIGKEIT
Natürlich ist die Rutschfestigkeit eine Eigenschaft, die sich im Bereich der Bodenbeläge auf die Sicherheit und Gesundheit der Anwender auswirkt. Rutschige Oberflächen sind mögliche Ursachen für unter
Umständen auch schwere Unfälle sowohl im zivilen Bereich als in der Arbeitsumgebung. Die Größe, die die Rutschfestigkeit misst, ist der Reibungskoeffizient (statisch und dynamisch). Zu diesen verhält sich
die Kraft proportional, die parallel zur Kontaktfläche wirkt und angewandt werden muss, damit eine relative Bewegung zwischen zwei Körpern erfolgt. Somit ist sie auch die Kraft, die die Bedingungen für
das Gleichgewicht bestimmt. Je höher der Reibungskoeffizient ist, umso niedriger ist die Rutschigkeit. Derzeit steht auf internationaler Ebene keine standardisierte Messmethode zur Verfügung. Der Großteil
der Länder besitzt eigene Methoden, die auf Gesetzen, Unfallschutzbestimmungen oder anderen Regelungen nationaler Art beruhen. Um ein gutes Ergebnis zu erzielen, muss der durchschnittliche Wert
des dynamischen Reibungskoeffizienten betragen: μ>0,40, R≥R9 und μ≥A.
Nachfolgend führen wir eine Zusammenfassung der Indikatoren auf, mit denen die Rutschfestigkeit gemessen wird:
R: gibt den beim Test erreichten Neigungswinkel an
A.B.C.: sind Bezüge der Rutschfestigkeit hinsichtlich Feuchträume und Füße
СТЕПЕНЬ ПРОТИВОСКОЛЬЖЕНИЯ
Устойчивость к скольжению - это характеристика, от которой зависит безопасность и здоровье потребителей, конечно, в случае, если речь идет о напольных покрытиях. Скользкие
поверхности являются потенциальной причиной несчастных случаев, иногда также тяжелых, как в жилых, так и в промышленных помещениях. Величиной, определяющей устойчивость к
скольжению, является коэффициент трения (статического или динамического), которому пропорциональна сила, параллельная контактной поверхности, которую необходимо приложить
для получения относительного движения между двумя телами, и, следовательно, также сила, которая определяет условия их равновесия. Чем больше коэффициент трения, тем меньше
способность к скольжению. В настоящее время не существует международного стандартного метода измерения этой величины, большинство государств использует свои собственные
методы, исходя из положений законов, норм техники безопасности или других национальных нормативов. Для получения хорошего результата среднее значение коэффициента
динамического скольжения должно составлять μ>0,40, R≥R9 und μ≥A.
Ниже перечислены показатели, измеряющие устойчивость к скольжению:
R: означает уклон, полученный при тестировании во время испытаний
A.B.C.: показатели устойчивости к скольжению во влажных помещениях и при движении босыми ногами.
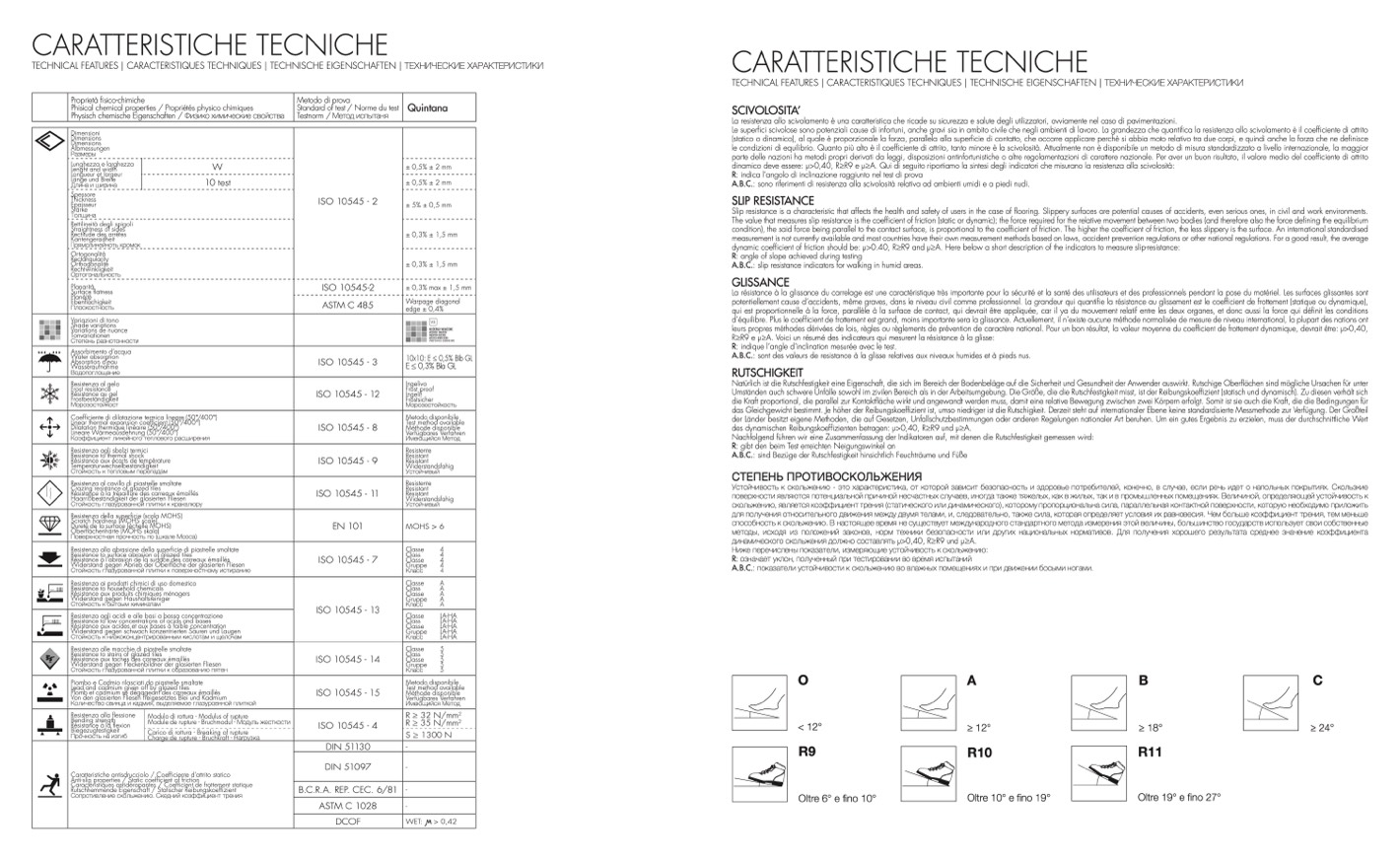
O
A
B
C
Proprietà fisico-chimiche
Phisical chemical properties / Propriétés physico chimiques
Physisch chemische Eigenschaften / Физико химические свойства
Metodo di prova
Standard of test / Norme du test
Testnorm / Meтод испытаня
ISO 10545 - 2
ISO 10545-2
ASTM C 485
ISO 10545 - 3
ISO 10545 - 12
ISO 10545 - 8
ISO 10545 - 9
ISO 10545 - 11
EN 101
ISO 10545 - 7
ISO 10545 - 13
ISO 10545 - 14
ISO 10545 - 15
ISO 10545 - 4
DIN 51130
DIN 51097
B.C.R.A. REP. CEC. 6/81
ASTM C 1028
DCOF
Quintana
± 0,5% ± 2 mm
± 0,5% ± 2 mm
± 5% ± 0,5 mm
± 0,3% ± 1,5 mm
± 0,3% ± 1,5 mm
± 0,3% max ± 1,5 mm
Warpage diagonal
edge ± 0,4%
MODERATA VARIAZIONE
MODERATE VARIATION
VARIATION MODEREE
MÄSSIGE ABWEICHUNG
УМЕРЕННОЕ ИЗМЕНЕНИЕ
10x10: E ≤ 0,5% BIb GL
E≤0,3%BIaGL
Ingelivo
Frost proof
Ingelif
Frostsicher
Морозостойкость
Metodo disponibile
Test method available
Méthode disponible
Verfügbares Verfahren
Имеющийся Метод
Resistente
Resistant
Résistant
Widerstandsfahig
Устойчивый
Resistente
Resistant
Résistant
Widerstandsfahig
Устойчивый
MOHS>6
Dimensioni
Dimensions
Dimensions
Albmessungen
Размеры
Lunghezza e larghezza
Lenght and width
Longueur et largeur
Länge und Breite
Длина и ширина
Spessore
Thickness
Epaisseur
Stärke
Толщина
Rettilineità degli spigoli
Straightness of sides
Rectitude des arrêtes
Kantengeradheit
Прямолинейноть кромок
Ortogonalità
Rectangularity
Orthogonalité
Rechtwinkligkeit
Ортогональность
Planarità
Surface flatness
Planéité
Ebenflächigkeit
Плоскостность
Variazioni di tono
Shade variations
Variations de nuance
Tonvariationen
Степень разнотонности
Assorbimento d’acqua
Water absorption
Absorption d’eau
Wasseraufnahme
Водопоглощение
Resistenza al gelo
Frost resistance
Résistance au gel
Frostbeständigkeit
Морозостойкост
W
10 test
Coefficiente di dilatazione termica lineare (50°/400°)
Linear thermal expansion coefficient (50°/400°)
Dilatation thermique linéaire (50°/400°)
Lineare Wärmeausdehnung (50°/400°)
Коэффициент линейного теплового расширения
Resistenza agli sbalzi termici
Resistance to thermal shock
Résistance aux écarts de température
Temperaturwechselbeständigkeit
Стойкость к тепловым перепадам
Resistenza al cavillo di piastrelle smaltate
Crazing resistance of glazed tiles
Résistance à la trésaillure des carreaux émaillés
Haarrißbeständigkeit der glasierten Fliesen
Стойкость глазурованной плитки к кракелюру
Resistenza della superficie (scala MOHS)
Scratch hardness (MOHS scale)
Dureté de la surface (échelle MOHS)
Oberflächenhärte (MOHS skala)
Поверхностная прочность по (шкале Мооса)
Resistenza alla abrasione della superficie di piastrelle smaltate
Resistance to surface abrasion of glazed tiles
Résistance à l’abrasion de la surface des carreaux émaillés
Widerstand gegen Abrieb der Oberfläche der glasierten Fliesen
Стойкость глазурованной плитки к поверхностному истиранию
Resistenza ai prodotti chimici di uso domestico
Resistance to household chemicals
Résistance aux produits chimiques ménagers
Widerstand gegen Haushaltsreiniger
Стойкость к бытоым химикатам
Resistenza agli acidi e alle basi a bassa concentrazione
Resistance to low concentrations of acids and bases
Résistance aux acides et aux bases à faible concentration
Widerstand gegen schwach konzentrierten Säuren und Laugen
Стойкость к низкоконцентрированным кислотам и щелочам
Resistenza alle macchie di piastrelle smaltate
Resistance to stains of glazed tiles
Résistance aux taches des carreaux émaillés
Widerstand gegen Fleckenbildner der glasierten Fliesen
Стойкость глазурованной плитки к образованию пятен
Piombo e Cadmio rilasciati da piastrelle smaltate
Lead and cadmium given off by glazed tiles
Plomb et cadmium se dégageant des carreaux émaillés
Von den glasierten Fliesen freigesetztes Blei und Kadmium
Количество свинца и кадмия, выделяемое глазуpoвнной плиткой
Classe
Class
4
Resistenza alla flessione
Bending strength
Résistance à la flexion
Biegezugfestigkeit
Прочность на изгиб
Modulo di rottura - Modulus of rupture
Module de rupture - Bruchmodul - Модуль жесткости
Carico di rottura - Breaking of rupture
Charge de rupture - Bruchkraft - Наrрузка
Classe
A
Class
A
Classe
A
Gruppe
A
Класс
A
Classe
LA-HA
Class
LA-HA
Classe
LA-HA
Gruppe
LA-HA
Класс
LA-HA
Classe
5
Class
5
Classe
5
Gruppe
5
Класс
5
Metodo disponibile
Test method available
Méthode disponible
Verfügbares Verfahren
Имеющийся Метод
R ≥ 32 N/mm
2
R ≥ 35 N/mm
2
S ≥ 1300 N
-
-
-
-
WET: > 0,42
< 12°
R9
Oltre 6° e fino 10°
≥ 12°
R10
Oltre 10° e fino 19°
≥ 18°
R11
Oltre 19° e fino 27°
≥ 24°
Caratteristiche antisdrucciolo / Coefficiente d’attrito statico
Anti-slip properties / Static coefficient of friction
Caractéristiques antidérapantes / Coefficient de frottement statique
Rutschhemmende Eigenschaft / Statischer Reibungskoeffizient
Сопротивление скольжению. Скедний козффициент трения
Classe
Gruppe
4
Класс
4
4
4